
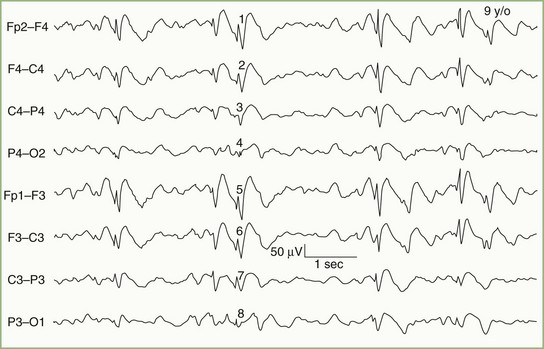
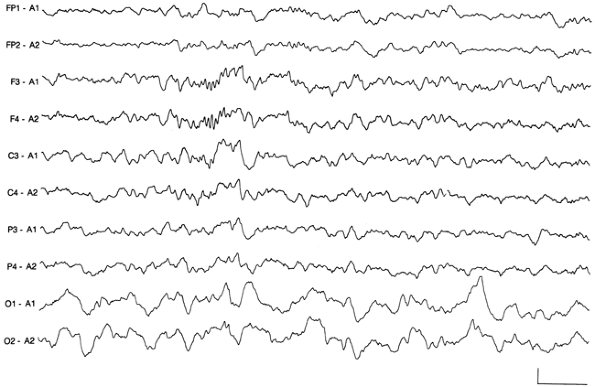
Summary of the types of abnormalities an EEG can detectĪ major question is whether resistance to standard treatment interventions is an indication to obtain an EEG. In general psychiatric practice, the leading indication for initiating some form of organic or neurological workup is an atypical presentation ( Figure). There are few psychiatric conditions in which the prevalence of epileptic activity has been documented to be elevated, and which warrant consideration of an EEG on the basis of presenting symptoms. The Table summarizes indications for which EEGs might prove useful for patients with psychiatric disorders. If slowing is suspected, the patient must be awake while the EEG is recorded if paroxysmal activity is suspected, the EEG needs to be done during both sleep and wake periods. Both kinds of abnormalities can be focal and suggestive of a localized pathological process, or generalized and more diffused, suggestive of a degenerative or metabolic process. The EEG may reveal 1 of 2 classes of deviations: the slowing of normal rhythms and the appearance of abnormal paroxysmal (episodic) electrical activity suggestive of an epileptic process. Indications for clinical EEGs in patients with psychiatric disorders Moreover, EEG discharges without overt seizures (ie, isolated epileptic discharges) may have behavioral consequences such as emotional lability, irritability, or temper dyscontrol that cut across broad diagnostic labels. Part of the reason that these patients have such a wide range of EEG abnormalities may be because the EEG signal is quite sensitive to many variables (eg, metabolic, vascular, endocrinological) that affect CNS function.Īlthough EEG abnormalities may not have direct primary psychiatric diagnostic specificity, they suggest the presence of other, organic/medical/physiological variables that could contribute to the psychiatric presentation. 1-4 EEG findings in psychiatric populations include generalized or focal slowing of cortical activity and a variety of focal or generalized paroxysmal EEG discharges. The prevalence of EEG abnormalities in psychiatric patients is significantly elevated and ranges from 20% to 68% higher than in healthy controls. While excessive beta during wakefulness has been linked with anxiety disorders, it is not considered an EEG abnormality (by today’s standards) and cannot be used to diagnose anxiety states. The appearance of excessive theta or any delta during wakefulness is a definite abnormality. When an adult begins to get drowsy, EEG rhythms slow to the theta (4 to 8 Hz) range and finally to the delta (below 4 Hz) range with sleep. Once the person focuses his or her attention or becomes stressed, the frequency increases to the beta range (above 13 Hz).
The EEG of an awake and relaxed healthy adult is usually dominated by frequencies between 8 and 13 cycles/second (8 to 13 Hz alpha activity). Increases the ability to detect various artifacts (ie, waveforms of non-brain origin) that can contaminate the recording.Permits recording arrays to locate focal or regional abnormal features more clearly.Allows direct comparisons between homologous cortical regions.The simultaneous recording of brain waves from many scalp locations is important because it: These EEG signals are the result of summated field potentials generated by excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials in vertically oriented pyramidal cells of the cortex. Electrical potentials measured between any 2 EEG electrodes fluctuate or oscillate rapidly, usually many times per second. Typical signals range from approximately 30 to 80 μV, but can be as low as 10 μV in some tracings or as high as 150 or 200 μV in some high-voltage “spike” epileptic discharges. The EEG is an extremely sensitive voltmeter. The abbreviated EEG can be done in a matter of minutes using a 10- or 12-channel recording instrument. A simplified EEG can have substantial diagnostic usefulness, particularly in emergency department settings. In conditions in which EEG abnormalities are demonstrably common, an EEG should be considered part of the essential workup. When the presentation is unusual, a neurological workup that includes an EEG is essential. The electroencephalogram (EEG) has a limited but definitive role in understanding and managing psychiatric conditions. CME credit for this article is now expired.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
